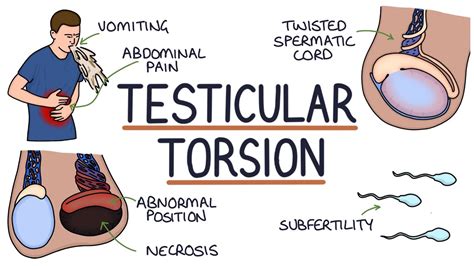
torsion of testes but testes move|testicular torsion symptoms in women : agent Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage.
webEvoPlay | 9,618 followers on LinkedIn. EvoPlay — leading developer of integrated products and solutions for the online gaming industry. Based on many years of experience in the segment of online .
{plog:ftitle_list}
26 de out. de 2022 · Aqui estão 7 desenhos do Gavião Arqueiro para imprimir e colorir: ⚡️ Pegue um atalho: O Gavião Arqueiro nas HQs: O Incrível Gavião Arqueiro: O Gavião Arqueiro e seus Poderes: 1. O que te .

Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle revolves and causes the spermatic cord from which it is suspended to twist and cut off blood flow to the testicle and scrotum. Often, testicular pain sets .Testicular torsion is a serious and painful condition that affects your testicle (s). If you experience testicular torsion, the spermatic cord twists and cuts off blood flow to your testicle. If you don’t .
Torsion can slow or cut off blood flow to your testicle. A lack of blood makes the affected testicle swell and become painful. Testicular torsion is a medical emergency. You . Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage the testicle, . Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. When a testicle (testis) twists around in the scrotum, the condition is called testicular torsion. An emergency operation is usually needed to treat this condition. In this .
Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or .
why does testicular torsion happen
Testicular torsion is a urological emergency. A high index of suspicion is important to ensure timely diagnosis and management. Increased public awareness is important in . The cremasteric reflex is most commonly performed in the evaluation of acute scrotal pain and the assessment for testicular torsion that is commonly associated with an apparent loss of the reflex.[1][2][3] . the cremaster muscle causes the testicles to move closer to the body. During fight or flight and sexual arousal, it is responsible for . Testicular torsion in newborns and infants. Testicular torsion can occur in newborns and infants, though it's rare. The infant's testicle might be hard, swollen or a darker color. Ultrasound might not detect reduced blood flow to the infant's scrotum, so surgery might be needed to confirm testicular torsion. Treatment for testicular torsion in .Testicular torsion can affect anyone who has testicles. However, 65% of all cases of testicular torsion occur in men and people AMAB between the ages of 12 and 18. You may be more likely to have testicular torsion if you’ve had one before or if someone in your biological family has had one. What are the complications of testicular torsion?
Testicular torsion is when your testicle twists around, cutting off its blood supply. It causes sudden, severe pain and swelling in your scrotum. . Some people have testicles that are held in place loosely inside their scrotum and can move more easily than for other people. This can lead to testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is also more .
torsion testis sign
Scrotal complaints are relatively common in the emergency department, comprising at least 0.5% of all emergency department visits. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to evaluate the . The spermatic cord provides blood flow to the testicle. Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates on this cord. . Having testicles that can rotate or move back and forth freely in the .
Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle revolves and causes the spermatic cord from which it is suspended to twist and cut off blood flow to the testicle and scrotum. Often, testicular pain sets in quickly, making it the key symptom. . This allows the testes to move around freely and twist. The added weight of the testicle after puberty may .
Testicular torsion in dogs is an uncommon condition but still has an appearance in veterinary clinics every so often. . Reluctant to move; Listlessness; Abnormal swelling of the affected testis or the scrotum . or a cryptorchid testicle. These testicles are more prone to move freely and rotate themselves within the scrotum or the lower . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. . clapper deformity which is the abnormally high attachment of the tunica vaginalis to the spermatic cord, allowing the testis and adjacent epididymis to move more freely, and thus places it at risk of twisting around the .
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates around the spermatic cord, which provides blood to the scrotum (a bag of skin that contains the testicles). . the testicle should move up ipsilaterally. With testicular torsion, this does not occur. Additional diagnostic methods include urine tests to exclude infection, scrotal ultrasound .Causes of testicle pain. Sudden, severe testicle pain can be caused by twisting of the testicle (testicular torsion). This is a serious problem that can lead to the loss of the testicle if it's not treated quickly. Less serious causes of testicle pain include: an infection (epididymitis) an injury; an inguinal hernia; a build-up of fluid (cyst) Introduction. Testicular torsion refers to the twisting of the spermatic cord within the scrotum. This leads to occlusion of testicular venous return and subsequent compromise of the arterial supply, resulting in ischaemia of the testis. 1. Testicular torsion is a urological emergency.Permanent ischaemic damage may occur within 4-8 hours and urgent surgical .
how do you use a plant moisture meter
Testicular torsion is seen most commonly in both young adults and babies that are four weeks old or younger. Testicular torsion in young adults is more common due to the bell clapper deformity. Bell clapper deformity is something that affects the spermatic cord in such a way to allow the testis to move more freely. Torsion occurs when the testis spins, twisting the spermatic cord, causing reduced blood flow and testicular damage. Timely surgery may be needed to save the testis.
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency when a testicle twists around the spermatic cord, cutting off the blood supply. While it can occur without pain, most people experience severe pain in the . Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without treatment the affected testicle will infarct within hours. Whilst theoretically it can occur at any age, peak incidence is in neonates and adolescents between the ages of .If a testicle has not descended, a surgeon will move the testicle into the scrotum and fasten it with sutures. Or, if the testicle has rotated and caused the spermatic cord from which it is suspended to twist, an orchiopexy may be performed to .
Testicular torsion is defined as a twisting of the testes or testicle on its connective tissue. It is also referred to as orchitis and epididymitis as these terms refer to symptoms of inflammation that are caused by infection, trauma or metastasis.If the fixation is too high (anterior and cephalad), the testes can move more freely and torsion is more likely. A: Fixation is normal. B: Fixation is too high, allowing the testis to rotate transversely and resulting in torsion. . Mellick LB, Sinex JE, Gibson RW, et al: A systematic review of testicle survival time after a torsion event . Scrotum and coverings of the testes Scrotum is a cutaneous (skin) sac that protects the testes. It consists of two layers: most superficially is the skin, and deeper is the dartos fascia.The dartos fascia contains muscle fibers that contract when it is cold, which results in wrinkling of the scrotal skin and brings the testes closer to the body. The result is a . evaluate for possible testicular torsion, . Ultrasound echoes can provide real-time still or moving images. Data from moving images is useful in examining blood flow to and from your testicles .
how does a garden moisture meter work
Inside the scrotum lie two testicles and a cord called the spermatic cord that delivers blood to the testicles. Testicular torsion is the twisting of this cord, and it restricts blood flow, causing the testicular tissues to die. Testicular torsion is the most common cause of male-related genital emergencies. While itTesticular torsion. The spermatic cord attaches the testicle to the body. Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord twists and cuts off the blood supply to the testicle. This condition can occur at any age, but tends to be more common between the onset of puberty and the mid-20s. It requires urgent medical attention.The main treatment for this condition is surgery to prevent further damage to the testicle and to keep torsion from reoccurring. The cause of testicular torsion is unknown, but it may arise if the testicle or the protective sac around the testicle is not completely attached to the scrotum, allowing it to move around freely. A retractile testicle is a testicle that tends to ‘retract’ or migrate up high in the scrotum or the groin, sometimes completely but temporarily disappearing from the scrotum for a period of time.This may occur with activity, during periods of emotional stress, or randomly. Sometimes, this is accompanied by a ‘shrinking scrotum‘ as well.. Positional discomfort, in .
The patient's presentation, including imaging and pathology, is diagnostic of testicular torsion. Testicular infarct following torsion is initially associated with conservation of germ cells; however, as congestion and hemorrhage increase, these cells slough into the lumens of seminiferous tubules and ultimately the entire tubule undergoes . A testicle that doesn't move down into its proper place in the scrotum before birth is called an undescended testicle. It's also known as cryptorchidism (krip-TOR-kih-diz-um). . Other health conditions linked with an undescended testicle include: Testicular torsion. This is the twisting of the cord that brings blood to the scrotum. It's a .
testicular torsion symptoms in women
WEBSe estás fora de Portugal e não queres perder os jogos do teu Clube, subscreve aqui a BTV e acompanha tudo no teu PC, Tablet ou Smartphone. Aderir à BTV. Adere à BTV .
torsion of testes but testes move|testicular torsion symptoms in women